Dr. Mahboob Ali :
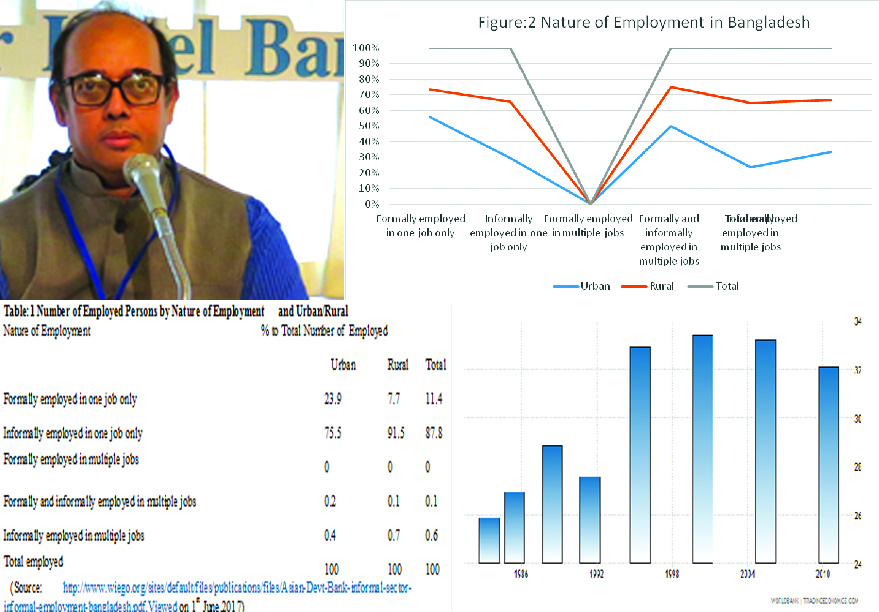
In the informal sector 87.8 percent totally is working while 11.4 percent is working in the formal sector. As per the following data formally employed in multiple job is zero percent. Formally and informally employed in multiple jobs is 0.1 percent in totality basis. Informally employed multiple jobs are totality basis is 0.6 percent. On the basis of Table:1 we have shown Figure:2 below.
Entrance to the formal monetary system leftovers to a contest for the underprivileged people of the country as existing financial system mostly ignoring them. Current banking system of the country has a missing services for a larger portion of the people. As such the country need alternative banking framework at a least cost combination and helping the underprivileged people. Moreover, some NGOs are not working due roles as they are charging higher interest rate which is not feasible for borrowers to repay without cutting welfare and social ignorance. Micro savings need to be encouraged to bring the unprivileged people to the banking system. With the introduction of the electronic banking current commercial banking rate is much higher.
We have shown Gini index of Bangladesh from 1986 to 2010 in Figure:3 below:
Need of the Study:
The study arises to develop a theoretical framework how social networking which is working for long historical background can help community based development purpose so that poor income strata of the people can have better livelihood. If only micro savings is accumulated but allocation and distribution cannot occur than it will be a burden for those who keep the money at their hand due to time value of money. Moreover, sometimes in the country multilevel marketing (MLM) companies are preying on regulatory and human weaknesses. They are managing funds and doing banking business illegally, but openly. Asset managers, merchant bankers, brokers or portfolio managers who manage others’ wealth are subject to government licence to operate (Daily Star, 2011). As such if community banking can be used under a regulatory basis then it may have a larger impact on transformation process of micro savings to micro investment and risk of theft-burglary will reduce.
Objectives of the Study:
The study has been undertaken with following objectives:
i)To assess whether any need for a new theory for doing economic development of poorer segment;
ii)To examine how social networking and community banking can help for attaining empowerment of people;
iii)To provide some suggestions for arranging distributional economic benefits and transformation from informal sector to formal sector.
Literature Review:
Acemogluand and Ozdaglar(2009)described that social and economic networks refers to a set of people or groups of people with some pattern of contacts or interactions between them. Face book, friendship networks, business relations between companies, intermarriages between families, labor markets. Recent years witnessed a substantial change in network research. From analysis of single small graphs (10-100 nodes) to statistical properties of large scale networks (million-billion nodes).Motivated by availability of computers and computer networks that allow us to gather and analyze large scale data. Gangopadhyay and Dhar (2014) described that social networking and online privacy seriously turn out to be a serious concern when sensitive information is being shared and with the changing definition of ‘social networking’ in this internet age. Riggio (2014) described that Social intelligence (SI), is mostly learned. SI develops from experience with people and learning from success and failures in social settings. It is more commonly referred to as “tact,” “common sense,” or “street smarts”. Lake and Huckfeldt (1998) argued that politically relevant social capital is generated in personal networks, that it is a by-product of the social interactions with a citizen’s discussants, and that increasing levels of politically relevant social capital enhance the likelihood that a citizen will be engaged in politics. Further, the production of politically relevant social capital is a function of the political expertise within an individual’s network of relations, the frequency of political interaction within the network, and the size or extensiveness of the network. The consequences of social relations within networks are not readily explained away on the basis of either human capital effects or the effects of organizational engagement. Actually social relations are very important. As such social intelligence and social entrepreneurship works with social networking. Social mixing should form an integral part of social intelligence development in teenagers. It argues that parents may have an important role to play, as older generations own circles also remain relatively closed to different cultures, backgrounds and upbringing.(Source:
http://movingonmagazine.co.uk/has-too-much-social-networking-stunted-your-social-intelligence/(Viewed on 1st January,2017). The success of a new venture often depends on an entrepreneur’s ability to establish a network of supportive relationships.
Leadbeater(1997) argues that social entrepreneurs need to lead the way with schemes for self-help, particularly by promoting local, national and international twinning arrangements between projects to share ideas, contacts and staff. For liberal feminists, the optimum level of gender arrangement is one that facilitates the individuals to adopt the life style that suits him or her and also accepted or respected (Ritzer, 2001) by the society at large. However, liberal feminists are not in favor of structural change to a great extent. Furthermore, some of liberal feminists think that individual woman cannot make change; therefore, state intervention is prerequisite. BarNirandSmith (2002)argued that the social networks of senior executives account for 11-22 % of the variance in the degree to which firms engage in alliances, depending on the type of alliance. Results also show that the number of inter firm alliances is positively related to several networking properties (propensity to network, strength of ties, and network prestige. Hunt and Kasynathan(2002) pointed out that only a few number of women receiving credit had the ability to control their loans. Many women received loan by their own name and passed on the full amount of their loans directly to their husbands, sons or sons-in-law. Swain (2006) conducted a study following experimental research design in rural India and assessed the potential impacts of a microfinance institution named Self Help Group (SHG). The concept of women empowerment was defined as the process in which the women challenge the existing norms and culture to effectively improve their well-being.
In the informal sector 87.8 percent totally is working while 11.4 percent is working in the formal sector. As per the following data formally employed in multiple job is zero percent. Formally and informally employed in multiple jobs is 0.1 percent in totality basis. Informally employed multiple jobs are totality basis is 0.6 percent. On the basis of Table:1 we have shown Figure:2 below.
Entrance to the formal monetary system leftovers to a contest for the underprivileged people of the country as existing financial system mostly ignoring them. Current banking system of the country has a missing services for a larger portion of the people. As such the country need alternative banking framework at a least cost combination and helping the underprivileged people. Moreover, some NGOs are not working due roles as they are charging higher interest rate which is not feasible for borrowers to repay without cutting welfare and social ignorance. Micro savings need to be encouraged to bring the unprivileged people to the banking system. With the introduction of the electronic banking current commercial banking rate is much higher.
We have shown Gini index of Bangladesh from 1986 to 2010 in Figure:3 below:
Need of the Study:
The study arises to develop a theoretical framework how social networking which is working for long historical background can help community based development purpose so that poor income strata of the people can have better livelihood. If only micro savings is accumulated but allocation and distribution cannot occur than it will be a burden for those who keep the money at their hand due to time value of money. Moreover, sometimes in the country multilevel marketing (MLM) companies are preying on regulatory and human weaknesses. They are managing funds and doing banking business illegally, but openly. Asset managers, merchant bankers, brokers or portfolio managers who manage others’ wealth are subject to government licence to operate (Daily Star, 2011). As such if community banking can be used under a regulatory basis then it may have a larger impact on transformation process of micro savings to micro investment and risk of theft-burglary will reduce.
Objectives of the Study:
The study has been undertaken with following objectives:
i)To assess whether any need for a new theory for doing economic development of poorer segment;
ii)To examine how social networking and community banking can help for attaining empowerment of people;
iii)To provide some suggestions for arranging distributional economic benefits and transformation from informal sector to formal sector.
Literature Review:
Acemogluand and Ozdaglar(2009)described that social and economic networks refers to a set of people or groups of people with some pattern of contacts or interactions between them. Face book, friendship networks, business relations between companies, intermarriages between families, labor markets. Recent years witnessed a substantial change in network research. From analysis of single small graphs (10-100 nodes) to statistical properties of large scale networks (million-billion nodes).Motivated by availability of computers and computer networks that allow us to gather and analyze large scale data. Gangopadhyay and Dhar (2014) described that social networking and online privacy seriously turn out to be a serious concern when sensitive information is being shared and with the changing definition of ‘social networking’ in this internet age. Riggio (2014) described that Social intelligence (SI), is mostly learned. SI develops from experience with people and learning from success and failures in social settings. It is more commonly referred to as “tact,” “common sense,” or “street smarts”. Lake and Huckfeldt (1998) argued that politically relevant social capital is generated in personal networks, that it is a by-product of the social interactions with a citizen’s discussants, and that increasing levels of politically relevant social capital enhance the likelihood that a citizen will be engaged in politics. Further, the production of politically relevant social capital is a function of the political expertise within an individual’s network of relations, the frequency of political interaction within the network, and the size or extensiveness of the network. The consequences of social relations within networks are not readily explained away on the basis of either human capital effects or the effects of organizational engagement. Actually social relations are very important. As such social intelligence and social entrepreneurship works with social networking. Social mixing should form an integral part of social intelligence development in teenagers. It argues that parents may have an important role to play, as older generations own circles also remain relatively closed to different cultures, backgrounds and upbringing.(Source:
http://movingonmagazine.co.uk/has-too-much-social-networking-stunted-your-social-intelligence/(Viewed on 1st January,2017). The success of a new venture often depends on an entrepreneur’s ability to establish a network of supportive relationships.
Leadbeater(1997) argues that social entrepreneurs need to lead the way with schemes for self-help, particularly by promoting local, national and international twinning arrangements between projects to share ideas, contacts and staff. For liberal feminists, the optimum level of gender arrangement is one that facilitates the individuals to adopt the life style that suits him or her and also accepted or respected (Ritzer, 2001) by the society at large. However, liberal feminists are not in favor of structural change to a great extent. Furthermore, some of liberal feminists think that individual woman cannot make change; therefore, state intervention is prerequisite. BarNirandSmith (2002)argued that the social networks of senior executives account for 11-22 % of the variance in the degree to which firms engage in alliances, depending on the type of alliance. Results also show that the number of inter firm alliances is positively related to several networking properties (propensity to network, strength of ties, and network prestige. Hunt and Kasynathan(2002) pointed out that only a few number of women receiving credit had the ability to control their loans. Many women received loan by their own name and passed on the full amount of their loans directly to their husbands, sons or sons-in-law. Swain (2006) conducted a study following experimental research design in rural India and assessed the potential impacts of a microfinance institution named Self Help Group (SHG). The concept of women empowerment was defined as the process in which the women challenge the existing norms and culture to effectively improve their well-being.