OhidulAlam :
Accidently, antibiotic (Penicillin) was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1929. To date, antibiotics have revolutionised medicine in many respects, and countless lives have been saved, their discovery was a turning point in human history. Regrettably, the use of these wonder drugs has been accompanied by the rapid appearance of resistant strains.
Antibiotics a type of antimicrobial used in the treatment and prevention of bacterial infection that may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. Several antibiotics are also effective against fungi and protozoans, and some are toxic to humans and animals. But, antibiotics are not effective against viruses’ and may be harmful when taken inappropriately.
Compared to population growth and economic development, production and consumption of such life-saving antibiotics are growing up indiscriminately since its invention. Due to multi-effectiveness, it is applied for curing human being from bacterial infected diseases as well for animals and plants. But, when a person or animal intake same antibiotic frequently then it kills susceptible bacteria but leaves resistance gene too.
Antibiotic resistance – is a natural phenomenon and it occurs when an antibiotic has lost its ability to effectively control or kill bacterial growth. When an antibiotic is used, bacteria that can resist that antibiotic have a greater chance of survival than those that are ‘susceptible.’ By the way, some bacteria achieve antibiotic resistance capacity known antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB). ARBs are such bacteria that are not controlled or killed by antibiotics. They are able to survive; even multiply in the presence of an antibiotic. Some bacteria have developed resistance to antibiotics that were once commonly used to treat them.
Some resistance occurs without human action, as bacteria can produce and use antibiotics against other bacteria, leading to a low-level of natural selection for resistance to antibiotics. However, the current higher-levels of ARBs are attributed to the overuse and abuse of antibiotics. Patients sometimes take antibiotics unnecessarily, to treat viral illnesses like the common cold. In addition, some bacteria are naturally resistant to certain types of antibiotics.
Any bacteria that acquire resistance genes, whether by spontaneous mutation or genetic exchange with other bacteria, have the ability to resist one or more antibiotics.
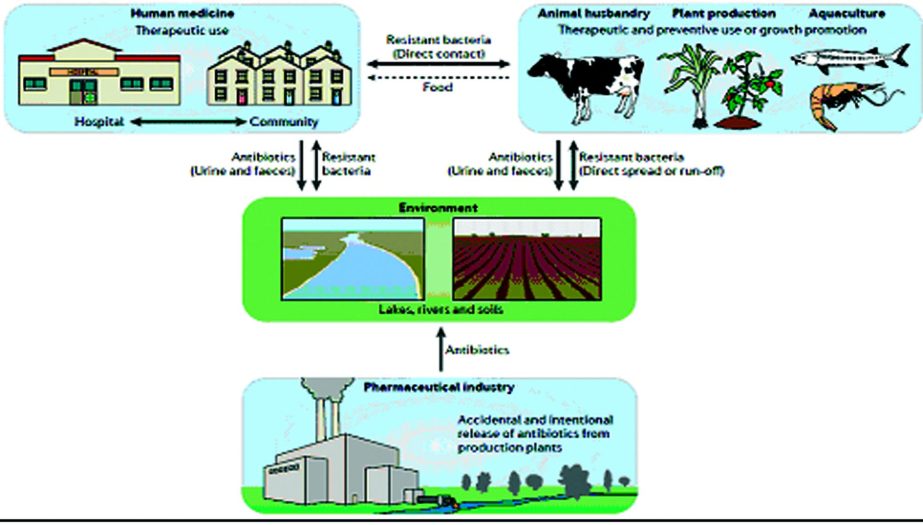
Lately, a new term ‘antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs)’ has already been introduced into environment which is currently considered as emerging contaminants posing a potential worldwide human health risk. The importance of bacterial isolates from wastewater environment as a reservoir of antibiotic resistance and a potential source of novel resistance genes to clinical pathogens is underestimated.
Intensive animal husbandry is believed to be a major contributor to the increased environmental burden of ARGs. Amidst, swine farms are known as hotspots for pervasive and abundant antibiotic resistance both in antibiotic-free animals and especially, in antibiotic-treated animals.
Genetically, antibiotic resistance spreads through bacteria populations both ‘vertically,’ when new generations inherit ARGs, and ‘horizontally,’ when bacteria share or exchange sections of genetic material with other bacteria. Environmentally, antibiotic resistance spreads as bacteria themselves move from place to place; bacteria can travel via airplane, water and wind. Similarly, people can pass the resistant bacteria to others; for example, by coughing or contact with unwashed hands.
Many researchers, especially in United States and China have already identified wastewater, surface water, river water, wastewater treatment plant, sludge, landfill leachate, soil, animal waste lagoon, and animal farm as reservoir of ARGs. Similarly, other agricultural countries like Bangladesh are in risk of ARGs spread but still not concerned about its silent long term environmental and health effect.
Currently, ARGs spread have become a global problem because it has increased the cost of life saving antibiotics. The emergence of drug-resistant bacterial strains is due to the selection pressure imposed by use of antibiotics.
The annual usage of antibiotics has been estimated to be 1 to 2 million tons globally, with more than 25,000 tons used each year in China. Large volume of antibiotic drug consumption is a major driver of antibiotic resistance in the environment. Besides, growing up antibiotic resistance capacity among bacteria depends on the – volumes and patterns of antibiotic consumption.
According to sales data of 71 countries, the consumption of standard units of antibiotics between 2000 and 2010 increased by 36 per cent where Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa accounted for 76 per cent of this increase. In most countries, antibiotic consumption varied significantly based on season. The rise of antibiotic consumption and the increase in use of last-resort antibiotic drugs raises serious – public health concern.
China is the largest antibiotics producer and consumers in the world; wherein 46.1 percent are used in livestock’s industries. Despite the volume of antibiotics used in China, little information is available regarding the corresponding ARGs associated with animal farms as well as other reservoirs.
On the contrary, surface water like river water and municipal or industrial wastewater as well landfill leachate are carrying considerable amount of ARGs which are ultimately intake into human body and causes health problems. In addition, application of organic manure also increases ARGs in farm soil. Since, still there is no control measures for spreading such ARGs; therefore, they are being silently distributed worldwide and intake into human body.
Moreover, conventional treatment processes are not suitable for removing or inactivating ARGs from wastewater, soil, and surface water etc. Therefore, ARGs are becoming emerging contamination globally by creating risks for human health and environment. Hence, researchers are searching for alternate and more appropriate technology for removing ARGs from such reservoirs to control further spreads.
However, diverse, abundant, and potentially mobile ARGs in farm samples suggest that unmonitored use of antibiotics and metals is causing the emergence and release of ARGs to the environment. Therefore, government should monitor production and consumption of antibiotics strictly. Similarly, antibiotics producers and consumers should be aware about the unnecessary consumption of antibiotics.
Bangladesh has a glorious history of exporting medicines worldwide. Hence, it’s produced medicine and antibiotics are exported in Asian countries, and Middle East countries, even in Europe. But still nobody has investigated about the associated ARGs risk with antibiotics production and subsequent effect in exporting countries.
Bangladesh is an agricultural country; therefore, a large volume of antibiotic is recently consumed in animal farms. Due to illiteracy, unnecessarily same amount of antibiotics are frequently used which is responsible for growing up antibiotics resistance capacity and ARBs; thus, silently it is distributing ARGs throughout the country. But mass people are not concerned about such health risks yet. n
(The author is student of IESD, Tongji University, China)
Accidently, antibiotic (Penicillin) was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1929. To date, antibiotics have revolutionised medicine in many respects, and countless lives have been saved, their discovery was a turning point in human history. Regrettably, the use of these wonder drugs has been accompanied by the rapid appearance of resistant strains.
Antibiotics a type of antimicrobial used in the treatment and prevention of bacterial infection that may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. Several antibiotics are also effective against fungi and protozoans, and some are toxic to humans and animals. But, antibiotics are not effective against viruses’ and may be harmful when taken inappropriately.
Compared to population growth and economic development, production and consumption of such life-saving antibiotics are growing up indiscriminately since its invention. Due to multi-effectiveness, it is applied for curing human being from bacterial infected diseases as well for animals and plants. But, when a person or animal intake same antibiotic frequently then it kills susceptible bacteria but leaves resistance gene too.
Antibiotic resistance – is a natural phenomenon and it occurs when an antibiotic has lost its ability to effectively control or kill bacterial growth. When an antibiotic is used, bacteria that can resist that antibiotic have a greater chance of survival than those that are ‘susceptible.’ By the way, some bacteria achieve antibiotic resistance capacity known antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB). ARBs are such bacteria that are not controlled or killed by antibiotics. They are able to survive; even multiply in the presence of an antibiotic. Some bacteria have developed resistance to antibiotics that were once commonly used to treat them.
Some resistance occurs without human action, as bacteria can produce and use antibiotics against other bacteria, leading to a low-level of natural selection for resistance to antibiotics. However, the current higher-levels of ARBs are attributed to the overuse and abuse of antibiotics. Patients sometimes take antibiotics unnecessarily, to treat viral illnesses like the common cold. In addition, some bacteria are naturally resistant to certain types of antibiotics.
Any bacteria that acquire resistance genes, whether by spontaneous mutation or genetic exchange with other bacteria, have the ability to resist one or more antibiotics.
Lately, a new term ‘antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs)’ has already been introduced into environment which is currently considered as emerging contaminants posing a potential worldwide human health risk. The importance of bacterial isolates from wastewater environment as a reservoir of antibiotic resistance and a potential source of novel resistance genes to clinical pathogens is underestimated.
Intensive animal husbandry is believed to be a major contributor to the increased environmental burden of ARGs. Amidst, swine farms are known as hotspots for pervasive and abundant antibiotic resistance both in antibiotic-free animals and especially, in antibiotic-treated animals.
Genetically, antibiotic resistance spreads through bacteria populations both ‘vertically,’ when new generations inherit ARGs, and ‘horizontally,’ when bacteria share or exchange sections of genetic material with other bacteria. Environmentally, antibiotic resistance spreads as bacteria themselves move from place to place; bacteria can travel via airplane, water and wind. Similarly, people can pass the resistant bacteria to others; for example, by coughing or contact with unwashed hands.
Many researchers, especially in United States and China have already identified wastewater, surface water, river water, wastewater treatment plant, sludge, landfill leachate, soil, animal waste lagoon, and animal farm as reservoir of ARGs. Similarly, other agricultural countries like Bangladesh are in risk of ARGs spread but still not concerned about its silent long term environmental and health effect.
Currently, ARGs spread have become a global problem because it has increased the cost of life saving antibiotics. The emergence of drug-resistant bacterial strains is due to the selection pressure imposed by use of antibiotics.
The annual usage of antibiotics has been estimated to be 1 to 2 million tons globally, with more than 25,000 tons used each year in China. Large volume of antibiotic drug consumption is a major driver of antibiotic resistance in the environment. Besides, growing up antibiotic resistance capacity among bacteria depends on the – volumes and patterns of antibiotic consumption.
According to sales data of 71 countries, the consumption of standard units of antibiotics between 2000 and 2010 increased by 36 per cent where Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa accounted for 76 per cent of this increase. In most countries, antibiotic consumption varied significantly based on season. The rise of antibiotic consumption and the increase in use of last-resort antibiotic drugs raises serious – public health concern.
China is the largest antibiotics producer and consumers in the world; wherein 46.1 percent are used in livestock’s industries. Despite the volume of antibiotics used in China, little information is available regarding the corresponding ARGs associated with animal farms as well as other reservoirs.
On the contrary, surface water like river water and municipal or industrial wastewater as well landfill leachate are carrying considerable amount of ARGs which are ultimately intake into human body and causes health problems. In addition, application of organic manure also increases ARGs in farm soil. Since, still there is no control measures for spreading such ARGs; therefore, they are being silently distributed worldwide and intake into human body.
Moreover, conventional treatment processes are not suitable for removing or inactivating ARGs from wastewater, soil, and surface water etc. Therefore, ARGs are becoming emerging contamination globally by creating risks for human health and environment. Hence, researchers are searching for alternate and more appropriate technology for removing ARGs from such reservoirs to control further spreads.
However, diverse, abundant, and potentially mobile ARGs in farm samples suggest that unmonitored use of antibiotics and metals is causing the emergence and release of ARGs to the environment. Therefore, government should monitor production and consumption of antibiotics strictly. Similarly, antibiotics producers and consumers should be aware about the unnecessary consumption of antibiotics.
Bangladesh has a glorious history of exporting medicines worldwide. Hence, it’s produced medicine and antibiotics are exported in Asian countries, and Middle East countries, even in Europe. But still nobody has investigated about the associated ARGs risk with antibiotics production and subsequent effect in exporting countries.
Bangladesh is an agricultural country; therefore, a large volume of antibiotic is recently consumed in animal farms. Due to illiteracy, unnecessarily same amount of antibiotics are frequently used which is responsible for growing up antibiotics resistance capacity and ARBs; thus, silently it is distributing ARGs throughout the country. But mass people are not concerned about such health risks yet. n
(The author is student of IESD, Tongji University, China)